Bradycardia
It is important for you to know how to recognise bradycardia and how to give appropriate treatment.
Select each heading to find out more.
The normal heart rate (ventricular rate) at rest is 60–100 beats min-1. A bradycardia is defined as a heart rate slower than 60 min-1.
Bradycardia may be:
- A physiological state in very fit people or during sleep
- An expected result of treatment (e.g. with a ß-blocker).
Pathological bradycardia may be caused by malfunction of the SA node or from partial or complete failure of atrioventricular conduction. Other pathological causes include vasovagal and other neurally-mediated syncope and presyncope and hypothyroidism.
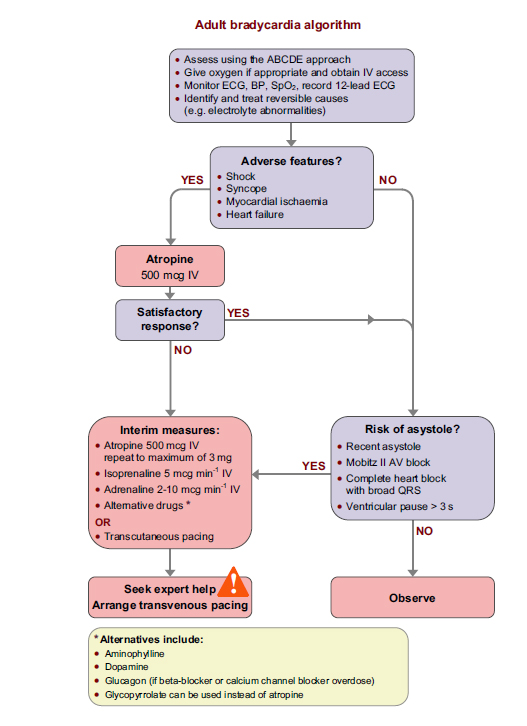
Select Next to continue.When you assess any patient with an arrhythmia address two factors:
- The condition of the patient (presence or absence of adverse features)
- The nature of the arrhythmia
Experience and expertise may be needed to identify some rhythm abnormalities with complete precision. However, a simple, structured approach to interpreting the rhythm on any ECG recording will define any rhythm in sufficient detail to enable the most appropriate treatment to be chosen.
Select Next to continue.Apply this to the analysis of any rhythm on an ECG:
1. Is there any electrical activity?
2. What is the ventricular (QRS) rate?
3. Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular?
4. Is the QRS width normal (narrow) or broad?
Any cardiac rhythm can be described accurately and managed safely and effectively using the first four stages.
5. Is atrial activity present? (If so, what is it: Typical sinus P waves? Atrial fibrillation? Atrial flutter? Abnormal P waves?)
6. How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? (e.g. 1:1 conduction, 2:1 conduction, etc, or no relationship)
Select Next to continue.
Extreme bradycardia may also cause such a severe fall in cardiac output to effectively cause cardiac arrest.
Select Next to continue.References
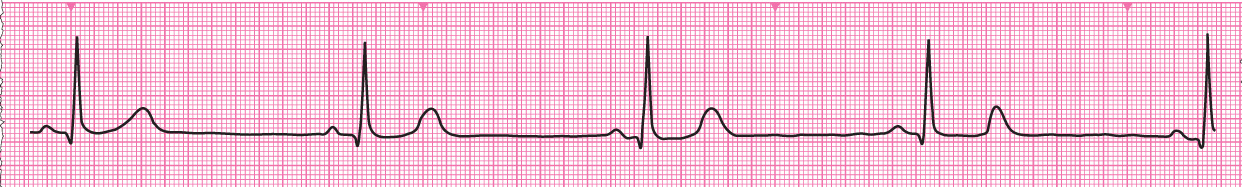
Rhythm strip showing Sinus bradycardia