
- Summary
You have reached the end of this case study on recognising types of tachycardia 2.

Here is a summary of the key points:
- If a patient has adverse features because of a tachyarrhythmia then vagal manoeuvres can be used whilst preparations are being made for synchronised cardioversion
- If vagal manoeuvres have been attempted and the arrhythmia persists then 6 mg of adenosine should be administered as a very rapid intravenous bolus
- If your patient does not respond to vagal manoeuvres or correctly prescribed doses of adenosine then you should seek expert help
References
See chapter 11 of the ALS manual for further reading about the tachycardia algorithm.
Essentials: The 6-stage approach
1. Is there any electrical activity?
2. What is the ventricular (QRS) rate?
3. Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular?
4. Is the QRS width normal (narrow) or broad?
Any cardiac rhythm can be described accurately and managed safely and effectively using the first four stages.
[hrule]
5. Is atrial activity present? (If so, what is it: Typical sinus P waves? Atrial fibrillation? Atrial flutter? Abnormal P waves?)
6. How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? (e.g 1:1 conduction, 2:1 conduction, etc, or no relationship)
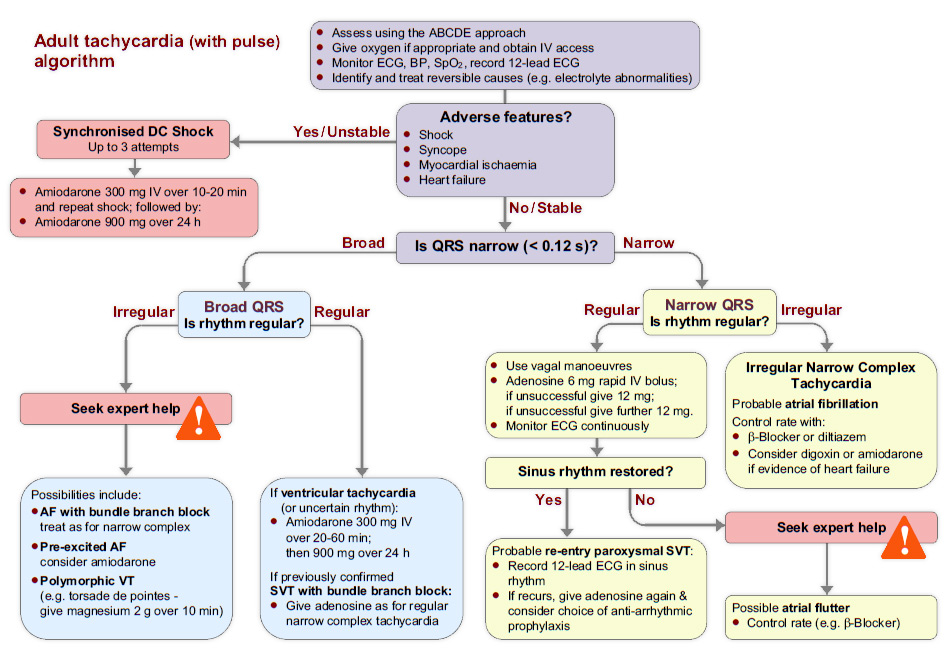
Algorithm: The tachycardia algorithm
The tachycardia algorithm is available in chapter 11 of the ALS manual.
Settings
Font colour
default inverted high contrast high contrast inverted high contrast soft green on blackSample text
text looks like thisTEXT LOOKS LIKE THIS
