Scenario three – next steps
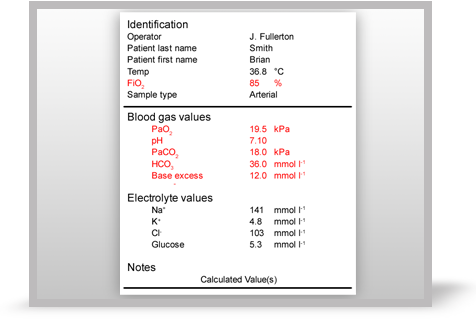
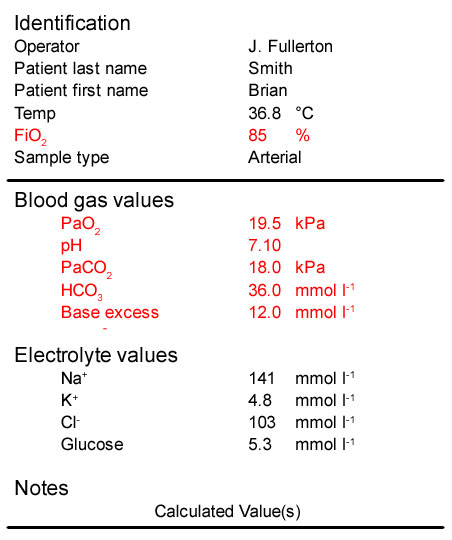
A colleague hands you the patient’s arterial blood gas results. What is your next step? Roll over the image to enlarge it.
Step 1: You should review how the patient is.
A patient with COPD who has had a respiratory arrest may have:
- Impaired oxygenation due to underlying lung disease
- A raised PaCO2 due to the period of apnoea and therefore have a respiratory acidosis
- Signs of compensation for his chronic respiratory acidosis due to COPD
Next you should continue to analyse this patient’s ABG results so that you can begin to determine the most appropriate course of action. Roll over the ABG print out to enlarge the results.
You can find the 5-step approach in the Essentials tab if you need a reminder.
Select Next to continue.5-step approach to ABG interpretation
Settings
Font colour
default inverted high contrast high contrast inverted high contrast soft green on blackSample text
text looks like thisTEXT LOOKS LIKE THIS