The ECG in acute myocardial infarction
Select two or more options and then select Confirm.

That is not quite right.
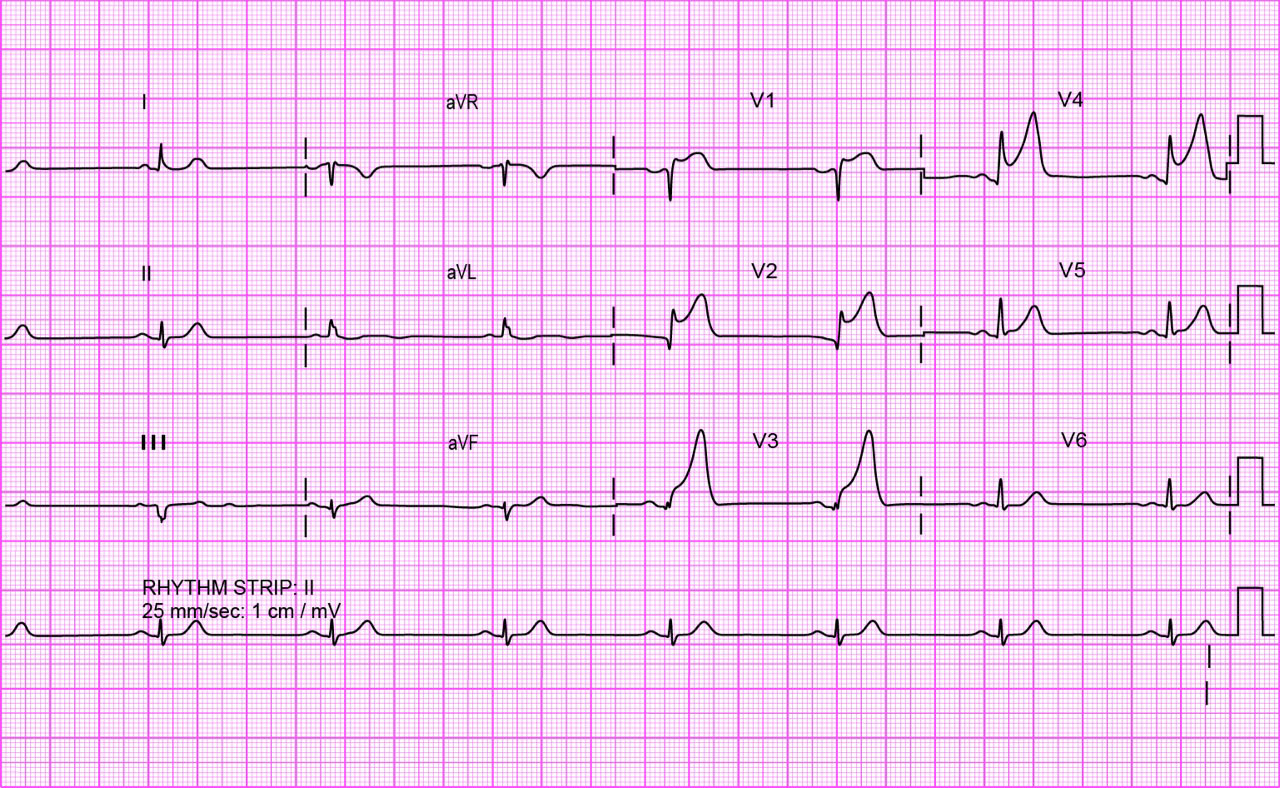
That is still not quite right. All these statements were true. ST segment elevation is present in leads V1-V4 so this is an anterior infarct. The rhythm is a regular narrow-complex bradycardia with a P wave before each QRS complex, indicating sinus bradycardia. Small but definite Q waves are present in the anterior leads. In a patient experiencing continuing pain from acute MI, an analgesic such as morphine is an important part of the immediate treatment, and as this is ST-segment-elevation MI immediate arrangements for reperfusion therapy are also indicated.
That is not right.
That is still not right. All these statements were true. ST segment elevation is present in leads V1-V4 so this is an anterior infarct. The rhythm is a regular narrow-complex bradycardia with a P wave before each QRS complex, indicating sinus bradycardia. Small but definite Q waves are present in the anterior leads. In a patient experiencing continuing pain from acute MI, an analgesic such as morphine is an important part of the immediate treatment, and as this is ST-segment-elevation MI immediate arrangements for reperfusion therapy are also indicated.
That is right. All these statements were true. ST segment elevation is present in leads V1-V4 so this is an anterior infarct. The rhythm is a regular narrow-complex bradycardia with a P wave before each QRS complex, indicating sinus bradycardia. Small but definite Q waves are present in the anterior leads. In a patient experiencing continuing pain from acute MI, an analgesic such as morphine is an important part of the immediate treatment, and as this is ST-segment-elevation MI immediate arrangements for reperfusion therapy are also indicated.
References
See chapter 8 of the ALS manual for further explanation and examples about how to analyse ECG rhythm strips.
The 6-stage approach
1. Is there any electrical activity?
2. What is the ventricular (QRS) rate?
3. Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular?
4. Is the QRS width normal (narrow) or broad?
Any cardiac rhythm can be described accurately and managed safely and effectively using the first four steps.
5. Is atrial activity present? (If so, what is it: Typical sinus P waves? Atrial fibrillation? Atrial flutter? Abnormal P waves?)
6. How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? (e.g 1:1 conduction, 2:1 conduction, etc, or no relationship)