
How to read a rhythm strip
Choose all the options that are correct and then select Confirm.

That is not quite right.
No, that is still not quite right. Description of any rhythm in terms of heart rate, regular or irregular rhythm and QRS width allows safe and effective treatment. After describing the rhythm in this way, identification of atrial activity should be attempted only when it is clearly present on the recording.
Broad QRS complexes may indicate bundle branch block, but will also be present in ventricular tachycardia and in broad-complex complete AV block.
The heart rate in AF will depend on the ability of the conducting system to transmit frequent electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles and on the use of drugs to slow the ventricular rate. Excessive effects of such drugs may cause bradycardia in the presence of AF and if there is no electrical conduction between atria and ventricles there will be complete heart block and the ventricular (QRS) rhythm will be a regular bradycardia.
Absence of electrical activity may be due to asystole, but may also be due to loss of electrical connection between the patient and the monitoring equipment, so should prompt an immediate check on the patient and the equipment.
That is not right.
No, that is still not right. Description of any rhythm in terms of heart rate, regular or irregular rhythm and QRS width allows safe and effective treatment. After describing the rhythm in this way, identification of atrial activity should be attempted only when it is clearly present on the recording.
Broad QRS complexes may indicate bundle branch block, but will also be present in ventricular tachycardia and in broad-complex complete AV block.
The heart rate in AF will depend on the ability of the conducting system to transmit frequent electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles and on the use of drugs to slow the ventricular rate. Excessive effects of such drugs may cause bradycardia in the presence of AF and if there is no electrical conduction between atria and ventricles there will be complete heart block and the ventricular (QRS) rhythm will be a regular bradycardia.
Absence of electrical activity may be due to asystole, but may also be due to loss of electrical connection between the patient and the monitoring equipment, so should prompt an immediate check on the patient and the equipment.
Yes, that is right. Description of any rhythm in terms of heart rate, regular or irregular rhythm and QRS width allows safe and effective treatment. Identification of atrial activity should be attempted only when it is clearly present on the recording.
References
See chapter 8 of the ALS manual for further explanation and examples about how to analyse ECG rhythm strips.
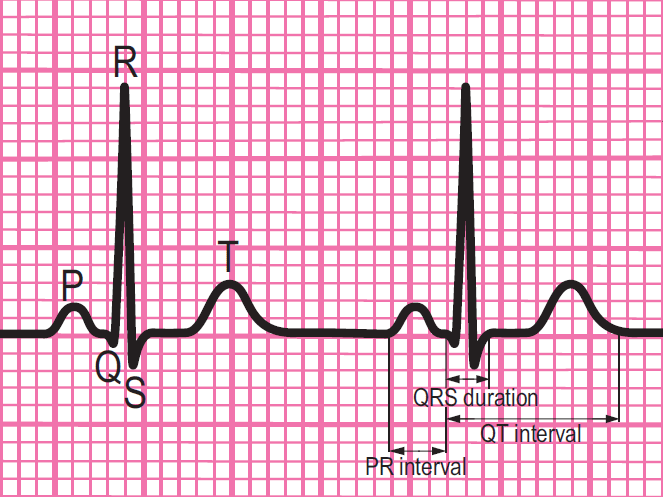
Components of a normal ECG complex
- Depolarisation begins in the SA node and then spreads through to the atrial myocardium
- The heart reacts to this depolarisation. The atrial contraction is recorded on the rhythm strip as the P wave
- The small isoelectric segment between the P wave and QRS complex represents the delay in transmission through the AV node
- Depolarisation of the bundle of His, bundle branches and ventricular myocardium is shown on the rhythm strip as the QRS complex
- The T wave represents recovery of the resting potential in the cells of the conducting system and ventricular myocardium

The 6-stage approach
1. Is there any electrical activity?
2. What is the ventricular (QRS) rate?
3. Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular?
4. Is the QRS width normal (narrow) or broad?
Any cardiac rhythm can be described accurately and managed safely and effectively using the first four steps.
5. Is atrial activity present? (If so, what is it: Typical sinus P waves? Atrial fibrillation? Atrial flutter? Abnormal P waves?)
6. How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? (e.g 1:1 conduction, 2:1 conduction, etc, or no relationship)




