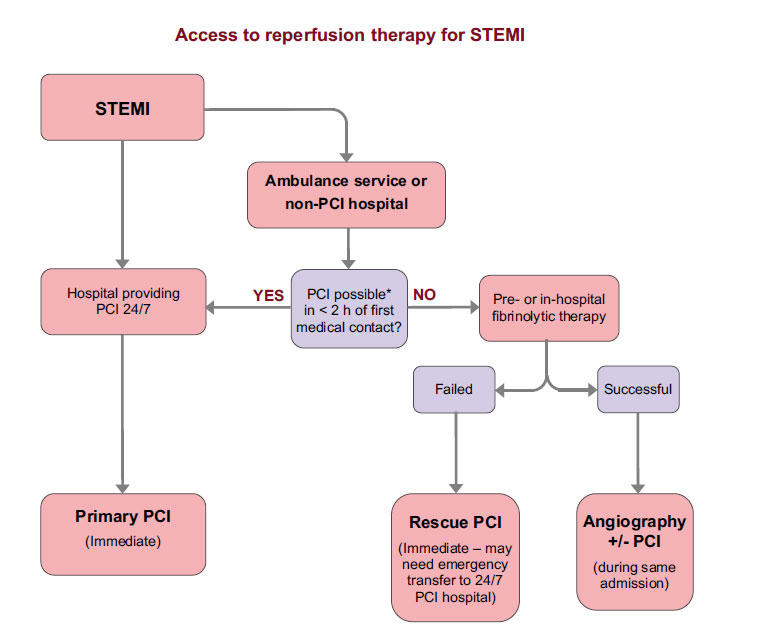
Acute ST-segment-elevation inferior myocardial infarction
Remember that when an acute coronary syndrome is suspected, the first priority is to look for ST segment elevation, because this usually implies occlusion of a coronary artery and the need for immediate reperfusion therapy.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more.

There is ST segment elevation in leads II, III and aVF, the inferior leads. In the presence of a clinical suspicion of an acute coronary syndrome this indicates acute inferior STEMI.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.

There is ST segment elevation in leads II, III and aVF, the inferior leads. In the presence of a clinical suspicion of an acute coronary syndrome this indicates acute inferior STEMI.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.

There is ST segment elevation in leads II, III and aVF, the inferior leads. In the presence of a clinical suspicion of an acute coronary syndrome this indicates acute inferior STEMI.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.

ST segment depression is present in leads I and aVL, in the presence of marked inferior ST segment elevation. In this setting, this appearance in these lateral leads is likely to represent reciprocal ST depression, reflecting ST segment elevation arising in the opposite wall of the left ventricle, rather than a problem in the lateral wall itself.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.

ST segment depression is present in leads I and aVL, in the presence of marked inferior ST segment elevation. In this setting, this appearance in these lateral leads is likely to represent reciprocal ST depression, reflecting ST segment elevation arising in the opposite wall of the left ventricle, rather than a problem in the lateral wall itself.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
Look at this ECG from a patient with severe chest pain. Click on the coloured circles to find out more. Select Next to continue.
References
See chapter 4 of the ALS manual for further detail relating to the assessment and treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes.
Acute coronary syndromes: immediate treatment and
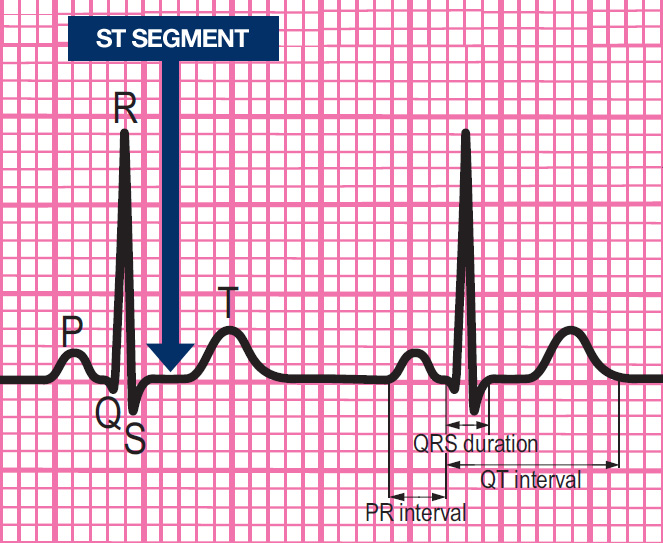
components of a normal ECG rhythm strip
Acute coronary syndromes: immediate treatment
Give immediate treatment to relieve symptoms, limits myocardial damage and reduce the risk of cardiac arrest. Immediate general treatment for ACS comprises:
- Aspirin
- Nitroglycerine
- Oxygen
- Morphine or Diamorphine
Components of a normal ECG complex
- Depolarisation begins in the SA node and then spreads through the atrial myocardium
- This depolarisation is recorded on the rhythm strip as the P wave. The heart responds to this electrical stimulus byatrial contraction
- The small isoelectric segment between the P wave and QRS complex represents the delay in transmission through the AV node
- Depolarisation of the bundle of His, bundle branches and ventricular myocardium is shown on the rhythm strip as the QRS complex
- The T wave represents recovery of the resting potential (repolarisation) in the cells of the conducting system and ventricular myocardium

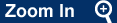
The ABCDE approach and access to reperfusion therapy for STEMI
Settings
Font colour
default inverted high contrast high contrast inverted high contrast soft green on blackSample text
text looks like thisTEXT LOOKS LIKE THIS