Patient five
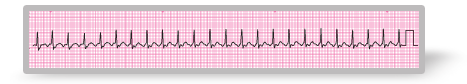
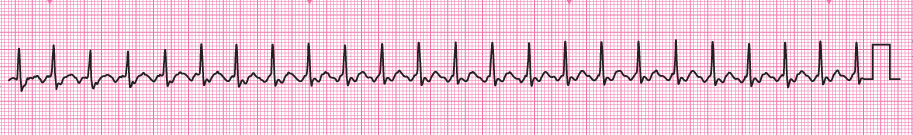
A patient with asthma has been admitted with increasing breathlessness despite increased treatment for his asthma. Following initial assessment an ECG monitor has been attached. Roll over the ECG to see a larger image.
Adrian Morel is a 55-year-old male who had a recent chest infection causing an exacerbation of his asthma. Following treatment with an antibiotic, steroids and increased bronchodilators his cough has settled and he feels less wheezy, but he is much more breathless on exertion than usual. Initial assessment has revealed:
A – Patent, able to speak normally
B – No obvious wheeze, RR 13 min-1. SpO2 96% on air
C – P regular, rate 150 min-1, BP 138/76 mm Hg, capillary refill 2s
D – Alert
E – No other abnormalities identified
You need to print off the rhythm strip to continue the assessment.
Select Next to continue.
A – Patent, able to speak normally
B – No obvious wheeze, RR 13 min-1. SpO2 96% on air
C – P regular, rate 150 min-1, BP 138/76 mm Hg, capillary refill 2s
D – Alert
E – No other abnormalities identified
You need to print off the rhythm strip to continue the assessment.
Select Next to continue.
References
See chapter 8 of the ALS manual for further explanation and examples of how to analyse cardiac rhythm from the ECG.
See chapter 11 of the ALS manual for further reading about the management of rhythm abnormalities.
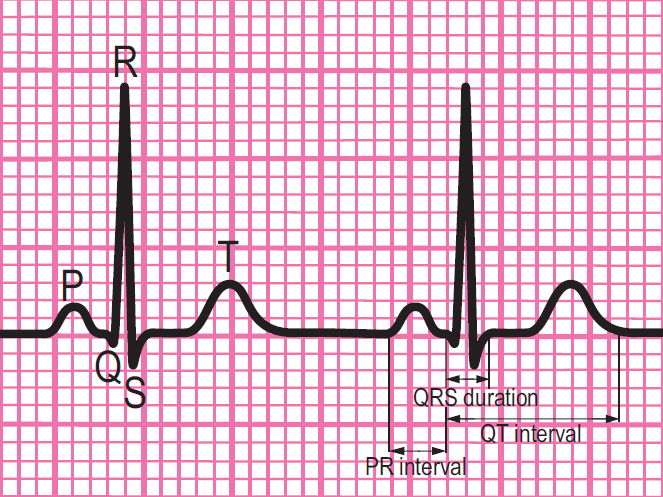
Components of a normal ECG complex
- Depolarisation begins in the SA node and then spreads through the atrial myocardium
- This depolarisation is recorded on the rhythm strip as the P wave. The heart responds to this electrical stimulus byatrial contraction
- The small isoelectric segment between the P wave and QRS complex represents the delay in transmission through the AV node
- Depolarisation of the bundle of His, bundle branches and ventricular myocardium is shown on the rhythm strip as the QRS complex
- The T wave represents recovery of the resting potential (repolarisation) in the cells of the conducting system and ventricular myocardium

The 6-stage approach
1. Is there any electrical activity?
2. What is the ventricular (QRS) rate?
3. Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular?
4. Is the QRS width normal (narrow) or broad?
Any cardiac rhythm can be described accurately and managed safely and effectively using the first four steps.
5. Is atrial activity present? (If so, what is it: Typical sinus P waves? Atrial fibrillation? Atrial flutter? Abnormal P waves?)
6. How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? (e.g 1:1 conduction, 2:1 conduction, etc, or no relationship)

Settings
Font colour
default inverted high contrast high contrast inverted high contrast soft green on blackSample text
text looks like thisTEXT LOOKS LIKE THIS