- Causes and prevention of cardiac arrest
Step 2
Learning outcomes
- The importance of early recognition of the deteriorating patient
- The causes of cardiac arrest in adults
- Identify and treat patients at risk of cardiac arrest using the ABCDE approach
Return to top
Step 3

Chain of survival
Early recognition prevents:
- Cardiac arrests and deaths
- Admissions to ICU
- Inappropriate resuscitation attempts
Return to top
Step 4

Early recognition of the deteriorating patient
- Most arrests are predictable
- Deterioration prior to 50 - 80% of cardiac arrests
- Hypoxia and hypotension are common antecedents
- Delays in referral to higher levels of care
Return to top
Step 5
- Source: National Cardiac Arrest Audit (NCAA) 2010
- Based on 3,184 adults (aged ≥ 16y) in 61 hospitals participating in NCAA (increasing numbers of hospitals during Oct 2009 to Oct 2010) with known presenting/first documented rhythm and complete data for ROSC and survival to hospital discharge. All these individuals received chest compressions and/or defibrillation from the resuscitation team in response to a 2222 call. Many in-hospital cardiac arrests do not fulfil these criteria and are not included here
- For full definitions, see NCAA Dataset Specification
Return to top
Step 6
This table can also be found in the Algorithm tab.
Return to top
Step 7
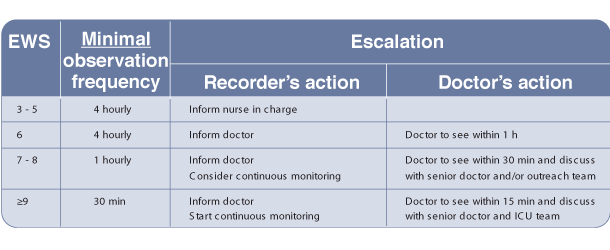
Recognition of the deteriorating patient - Early Warning Scoring (EWS) systems
Example Escalation Protocol based on an EWS
Return to top
Step 9
ABCDE approach
Underlying principles:
- Complete initial assessment
- Treat life-threatening problems
- Reassessment
- assess effects of treatment/interventions
- Call for help early
Return to top
Step 10
ABCDE approach
- Personal safety
- Patient responsiveness
- First impression
- Vital signs
- respiratory rate, SpO2, pulse, BP, GCS, temperature
Return to top
Step 11
ABCDE approach
Airway
Causes of airway obstruction:
- CNS depression
- Blood
- Vomit
- Foreign body
- Trauma
- Infection
- Inflammation
- Laryngospasm
- Bronchospasm
Return to top
Step 12
ABCDE approach
Airway
Recognition of airway obstruction:
- Talking
- Difficulty breathing, distressed, choking
- Shortness of breath
- Noisy breathing
- stridor, wheeze, gurgling
- See-saw respiratory pattern, accessory muscles
Return to top
Step 13
ABCDE approach
Airway
Treatment of airway obstruction:
- Airway opening
- head tilt, chin lift, jaw thrust
- Simple adjuncts
- Advanced techniques
- e.g. LMA, tracheal tube
- Oxygen
Return to top
Step 14
ABCDE approach
Breathing
Causes of breathing problems:
- Decreased respiratory drive
- CNS depression
- Decreased respiratory effort
- muscle weakness
- nerve damage
- restrictive chest defect
- pain from fractured ribs
- Lung disorders
- pneumothorax
- haemothorax
- infection
- acute exacerbation COPD
- asthma
- pulmonary embolus
- ARDS
Return to top
Step 15
ABCDE approach
Breathing
Recognition of breathing problems:
- Look
- respiratory distress, accessory muscles, cyanosis, respiratory rate,
chest deformity, conscious level
- respiratory distress, accessory muscles, cyanosis, respiratory rate,
- Listen
- noisy breathing, breath sounds
- Feel
- expansion, percussion, tracheal position
Return to top
Step 16
ABCDE approach
Breathing
Treatment of breathing problems:
- Airway
- Oxygen
- Treat underlying cause
- e.g. drain pneumothorax
- Support breathing if inadequate
- e.g. ventilate with bag-mask
Return to top
Step 17
ABCDE approach
Circulation
Causes of circulation problems:
- Primary
- acute coronary syndromes
- arrhythmias
- hypertensive heart disease
- valve disease
- drugs
- hereditary cardiac diseases
- electrolyte/acid base abnormalities
[nbsp]
[nbsp]
- Secondary
- asphyxia
- hypoxaemia
- blood loss
- hypothermia
- septic shock
Return to top
Step 18
ABCDE approach
Circulation
Recognition of circulation problems:
- Look at the patient
- Pulse - tachycardia, bradycardia
- Peripheral perfusion - capillary refill time
- Blood pressure
- Organ perfusion
- chest pain, mental state, urine output
- Bleeding, fluid losses
Return to top
Step 19
ABCDE approach
Circulation
Treatment of circulation problems:
- Airway, breathing
- Oxygen
- IV/IO access, take bloods
- Treat cause
- Fluid challenge
- Haemodynamic monitoring
- Inotropes/vasopressors
- Aspirin/nitrates/oxygen
(if appropriate) and morphine
for acute coronary syndrome
Return to top
Step 20
ABCDE approach
Disability
Recognition
- AVPU or GCS
- Pupils
Treatment
- ABC
- Treat underlying cause
- Blood glucose
- if < 4 mmol l-1 give glucose
- Consider lateral position
- Check drug chart
Return to top
Step 21
ABCDE approach
Exposure
- Remove clothes to enable examination
- e.g. injuries, bleeding, rashes
- Avoid heat loss
- Maintain dignity
Return to top
Step 22
Summary
- Early recognition of the deteriorating patient may prevent cardiac arrest
- Most patients have warning symptoms and signs before cardiac arrest
- Airway, Breathing or Circulation problems can cause cardiac arrest
- ABCDE approach to recognise and treat patients at risk of cardiac arrest
Return to top
Step 23
Advanced Life Support Course
E-lecture
All rights reserved
© Resuscitation Council (UK) 2011
Return to top
Transcript
1. Causes and prevention of cardiac arrest.
2. The learning outcomes of this lecture are to understand:
- The importance of early recognition of the deteriorating patient
- The causes of cardiac arrest in adults
- How to identify and treat patients at risk of cardiac arrest using the ABCDE approach
3. Early recognition and a call for help to prevent cardiac arrest is the first link in the chain of survival.
For patients in-hospital this may prevent cardiac arrest and death, and prevent admissions to the intensive care unit.
Early identification can also identify patients who would not benefit from resuscitation or do not wish to be resuscitated. This will prevent inappropriate resuscitation attempts.
4. Studies show that 50-80% of in-hospital cardiac arrest patients have a period of deterioration before the cardiac arrest.
Hypoxia and hypotension are common antecedents, and there are often delays in escalating treatments, or in referring the patient to intensive care or outreach teams.
This observation chart is from a patient who had a cardiac arrest.
The patient has an increasing respiratory rate, a falling oxygen saturation despite oxygen therapy, an increasing pulse and falling systolic blood pressure in the hours before the cardiac arrest.
Earlier recognition of deterioration and early treatment may have prevented this patient’s cardiac arrest.
Once cardiac arrest occurs, survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest depends on the victim’s initial cardiac arrest rhythm and location of the arrest.
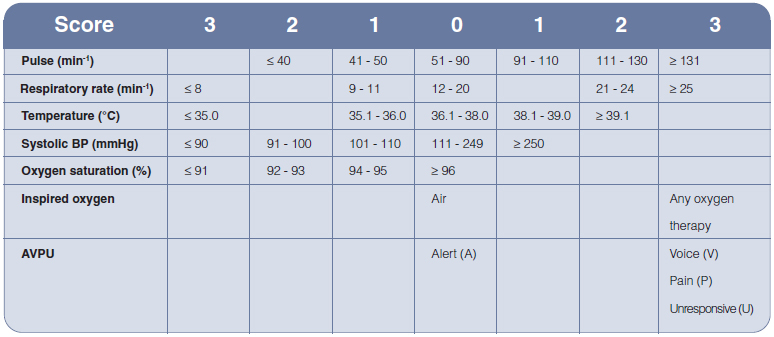
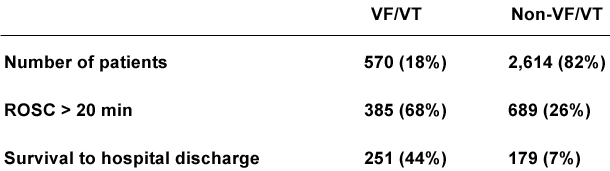
5. The table shows initial data for the National Cardiac Arrest Audit in the UK.
Survival to hospital discharge after a VF/VT cardiac arrest is 44%.
However most cardiac arrests, 82% in this data set, have non VF/VT arrests and survival to discharge is poor, about 7%.
Non VF/VT arrests or PEA and asystole tend to occur more commonly in ward areas and often have a period of deterioration before hand.
Prevention of cardiac arrest is very important for this group.
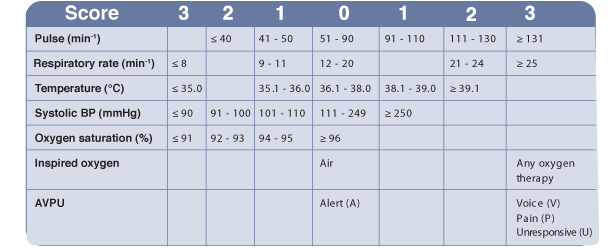
6. The use of early warning scoring systems to help recognise the deteriorating patient is now common in hospitals.
There are several early warning systems available and you need to be familiar with the one used in your hospital.
The table shows one example of an early warning scoring system.
When the patient’s observations are taken, the early warning score is calculated.
So for example, a pulse of 120 would score 2 points, a respiratory rate of 20, 0 points, a temperature of 38.2, 1 point, and so on.
The total number of points from all the observations is then added up and the total score is used to plan further actions.
The higher the score the greater the risk of further deterioration, cardiac arrest and need for urgent treatments.
7. This table gives an example of an escalation protocol based on the early warning score.
So, if the patient has an early warning score of 7, the doctor should be informed, and the need for continuous monitoring considered.
The doctor must see the patient within 30 minutes and discuss the patient with a senior doctor and/or the outreach team to make a treatment plan. If this doesn’t happen the doctor should be chased up, or a more senior doctor contacted.
Failure to escalate early is a common cause of cardiac arrest in the deteriorating patient.
8. We will now discuss Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure; this is commonly referred to as the ABCDE approach. It is used to recognise and treat the deteriorating patient.
9. The underlying principles of the ABCDE approach are:
- firstly, to complete the initial assessment
- secondly, to treat life-threatening problems as they are identified
- thirdly, to frequently reassess the patient to assess the effects of treatments and interventions
- lastly, but importantly, the need to call for help early
10. Also, don’t forget your personal safety – wear gloves, aprons and other protective equipment as appropriate.
Check the patient’s responsiveness – talk to him and shake and shout if he does not respond.
Your first impression is very important – if the patient looks very unwell, the chances are he is very unwell.
Monitor and record vital signs including respiratory rate, the oxygen saturation, the pulse, blood pressure, conscious level using the Glasgow coma score, and temperature.
Usually several people are present so you can do more than one thing at the same time.
11. I will now discuss each component of the ABCDE approach.
Airway obstruction has a variety of causes.
A decreased conscious level is a common cause, for example after sedative drugs.
Other causes are listed.
Bronchospasm causes obstruction of the lower airways.
12. Airway obstruction is unlikely, for the time being at least, if the person can talk normally.
If a person has airway obstruction they will find it difficult to breath, may be distressed, or choking and there may be shortness of breath.
The breathing can also be noisy with stridor, wheeze or gurgling.
The victim may have a see-saw respiratory pattern and use his accessory muscles.
13. Treatments for airway obstruction include:
- airway opening manoeuvres such as the head tilt with chin lift, or the jaw thrust
- the use of simple adjuncts such as oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways
- supraglottic airway devices, such as the laryngeal mask airway or igel
- and finally, tracheal intubation
The techniques you will use depend on the patient’s condition and your own skills and experience – indeed only those experienced in tracheal intubation should intubate.
Remember to give oxygen – the amount of oxygen given should be adjusted so that the patient has a normal oxygen saturation.
14. Breathing problems can occur because:
- there is decreased respiratory drive, such as in CNS depression after a drug overdose
- there is decreased respiratory effort, such as in muscle weakness or nerve damage
- the patient has a restrictive chest defect or pain from fractured ribs
And finally if there are primary lung disorders such as a pneumonia or an acute exacerbation COPD, asthma, or pulmonary embolus.
15. Use the Look, Listen and Feel approach to recognize breathing problems.
Look for respiratory distress, use of accessory muscles, cyanosis, a fast respiratory rate, chest deformity, or a reduced conscious level.
Listen for noisy breathing and to breath sounds.
Feel for chest expansion, percuss the chest, and check tracheal position.
16. Treatment of breathing problems includes:
- first ensuring there are no airway problems
- remembering to give oxygen so that the oxygen saturation is normal for the patient
- treating the underlying cause - for example, draining a pneumothorax
If the patient is not breathing, support their ventilation, for example, by using a bag mask.
17. Circulation problems can be primary or secondary:
Primary problems include:
- acute coronary syndromes
- arrhythmias
- hypertensive heart disease
- valve disease
- the effect of drugs on the heart
- hereditary cardiac diseases
- the effects of electrolyte and acid base abnormalities
Causes of secondary problems to the circulation include:
- asphyxia
- hypoxaemia
- blood loss
- hypothermia
- septic shock
18. To recognise circulation problems, first look at the patient. Assess the pulse rate - the patient may have a tachycardia or bradycardia. You can check the capillary refill time to assess peripheral perfusion. And remember to measure the blood pressure.
Also, don’t forget that chest pain, confusion or a poor urine output can all indicate poor organ perfusion caused by a circulation problem.
Look for bleeding or other fluid losses such as diarrhoea.
19. Treat circulation problems by first ensuring there are no airway or breathing problems.
Give oxygen if needed to maintain a normal oxygen saturation.
Obtain IV access and take bloods for lab tests.
Treat the underlying cause – for example, percutaneous coronary intervention after ST elevation myocardial infarction.
Give a fluid challenge and assess the response if the blood pressure is low.
Start haemodynamic monitoring.
Patients who remain hypotensive may benefit from inotropes and vasopressors.
If an acute coronary syndrome is suspected give aspirin/nitrates/oxygen, if appropriate, and morphine for the pain.
20. Disability problems are often caused by Airway, Breathing or Circulation problems, so ensure these have been recognized and treated.
Assess conscious level by using AVPU or the Glasgow Coma Scale score.
For AVPU, A stands for Alert, V for responds to Voice, P for responds to pain, and U for unresponsive.
The Glasgow Coma Scale score is based on the best score for eye opening, verbal response and motor response - a normal score is 15 and the lowest possible score is 3.
As mentioned earlier identify and treat any underlying ABC cause such as giving fluids for hypotension. Don’t forget to check the blood glucose and treat a low blood glucose with IV glucose.
An unconscious patient is at risk of aspirating gastric contents into his lungs – consider nursing the patient sitting up or in the lateral position to reduce this risk.
Always check the patient’s drug chart – ensure they are not on any drugs that decrease conscious level.
21. The E is for Exposure to ensure that you do a full assessment, including removing the patient’s clothes if necessary.
Look for injuries, rashes, evidence of bleeding.
Make sure you maintain the patient’s dignity at all times.
22. In summary, these are the key points for Causes and Prevention of Cardiac Arrest:
- early recognition of the deteriorating patient can prevent cardiac arrest
- most patients have warning symptoms and signs before cardiac arrest
- airway, Breathing or Circulation problems can cause cardiac arrest
- use the ABCDE approach to recognise and treat patients at risk of cardiac arrest
Credits
Dr Jasmeet Soar is a member of the Resuscitation Council (UK) ALS Subcommittee, Chair of the ILS Subcommittee and the current Chair of the Council. He is a Task Force Co-Chair for the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) and an Editor for the journal 'Resuscitation'. He is a Consultant in Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine at the North Bristol NHS Trust. (2011)
You have reached the end of this presentation. Either use the controls to revisit the presentation, select Menu to return to the module menu or Home/Exit to return to main course menu.
References
See chapter 3 of the ALS manual for further reading about the causes and prevention of cardiac arrest and the ABCDE approach.
Essentials: The ABCDE Approach
Algorithm: Example of an EWS system
* From Prytherch et al. ViEWS—Towards a national early warning score for detecting adult in-patient deterioration. Resuscitation. 2010;81(8):932-7