Escape and agonal rhythms
There are two other rhythms which are relevant to bradycardia.
Select each heading to find out more.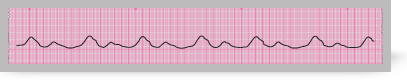
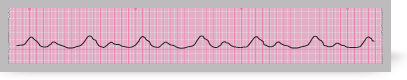
Agonal rhythm occurs in dying patients.
It is characterised by the presence of slow, irregular, wide ventricular complexes, often of varying morphology. The section from an ECG rhythm strip here shows agonal rhythm.
This rhythm is seen commonly during the later stages of unsuccessful resuscitation attempts. The complexes slow inexorably and often become progressively broader before all recognisable activity is lost.
Select Menu to return to the main menu.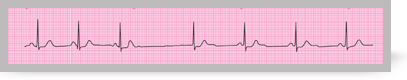
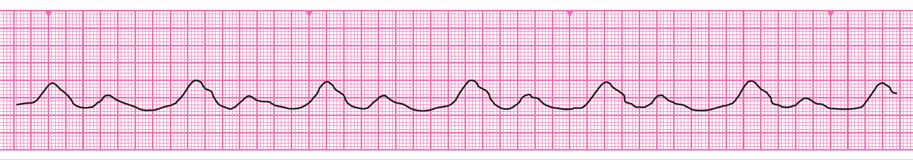
If the normal cardiac pacemaker (SA node) fails, or operates abnormally slowly, cardiac depolarisation may be initiated from a ‘subsidiary’ pacemaker in atrial myocardium, AV node, conducting fibres or ventricular myocardium.
The resulting escape rhythm will, in most cases, be slower than the normal sinus rate.
Select Menu to return to the main menu.References
See chapter 8 of the ALS manual for further reading about estimating the heart rate, QRS and cardiac arrest rhythms, heart blocks and bradyarrhythmia.